Community
osapeers.org
This article is available in
About this article

Hardik Agrawal
AuthorAssigned categories
Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly frequent and sophisticated across the EU, yet fewer than one in three organizations feel prepared to prevent or manage them. As digital threats intensify, the EU has made cybersecurity a long-standing priority, introducing a series of regulations to strengthen resilience and protect critical infrastructure.
The original NIS Directive aimed to raise cybersecurity standards through improved national capabilities, stronger cross-border cooperation, and clear risk management and incident reporting rules. However, it applied only to a limited group of essential service providers, which left many sectors unregulated and vulnerable. To address these gaps, the European Commission revised the directive, leading to the adoption of NIS2.
The Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2) entered into force on January 16, 2023. As a continuation and expansion of the previous cybersecurity directive, NIS2 was brought into effect to expand the scope and rectify the deficiencies of the original NIS directive.
NIS2 continues to focus on strengthening the security of network and information systems across the EU. It broadens the directive’s scope, raises cybersecurity standards, and introduces stricter rules for reporting, governance, and supply chain oversight.
The NIS2 Directive sets out definitive rules within the following four main areas: Risk Management, Reporting Obligations, Corporate Accountability, and Business Continuity. Non-compliance within these areas leads to strict penalties. Here’s a rundown of these primary areas in more detail.
The directive introduces measures to strengthen cyber risk management and mitigation. It does not prescribe specific technologies but defines key outcomes and control areas that organizations must address, particularly in the following areas:
Within the NIS2, senior management is directly accountable for compliance. It places explicit responsibility at the top, making cybersecurity a boardroom priority rather than an operational afterthought. Management must lead, approve, monitor, and be able to prove their active involvement in compliance. Here are some specific measures that leadership teams should take:
Companies are required to promptly report any cybersecurity related incidents to the appropriate national authorities. A brief overview of the timeline:
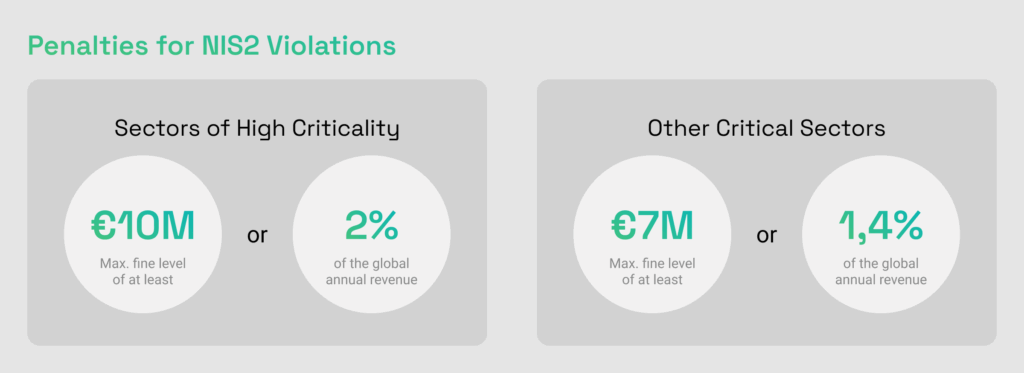
For the post incident recovery process, organizations should prepare a structured business continuity plan, which may include the following steps:
The sectors within NIS2 are categorized based on High Criticality and Other Critical Sectors (as stated in Annex I & Annex II). Refer to the infographic below for a detailed insight into the sectors within the updated scope of NIS2.
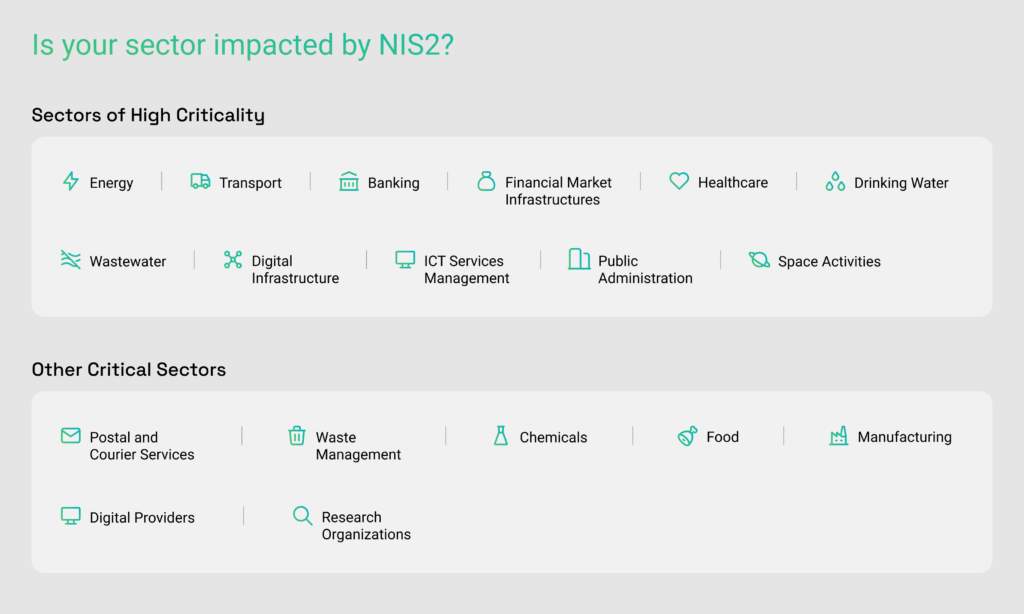
Due to an increase in the number of sectors, a larger number of public and private entities are now covered by the NIS2 directive. Here’s how you can check if your company falls within the scope of the directive:
The osapiens HUB for NIS2 provides a streamlined, scalable solution to help businesses of all sizes meet the directive efficiently and transparently. Developed with cybersecurity experts from VICCON, it is legally compliant by design and fully aligned with NIS2 requirements, with optional expert consulting available.
The solution combines risk management, procurement, and supplier governance in one platform, covering ESG topics, cyber risks, and more. Features such as risk analysis, incident reporting, case management, and automation make it easy to verify and document supplier compliance. Guided workflows reduce manual effort, fit seamlessly into existing structures, and simplify even complex processes.
Is your business ready to meet the evolving NIS2 requirements with confidence? Start your journey today with the osapiens HUB for NIS2 and benefit from a single, integrated platform built for security, efficiency, and transparency.